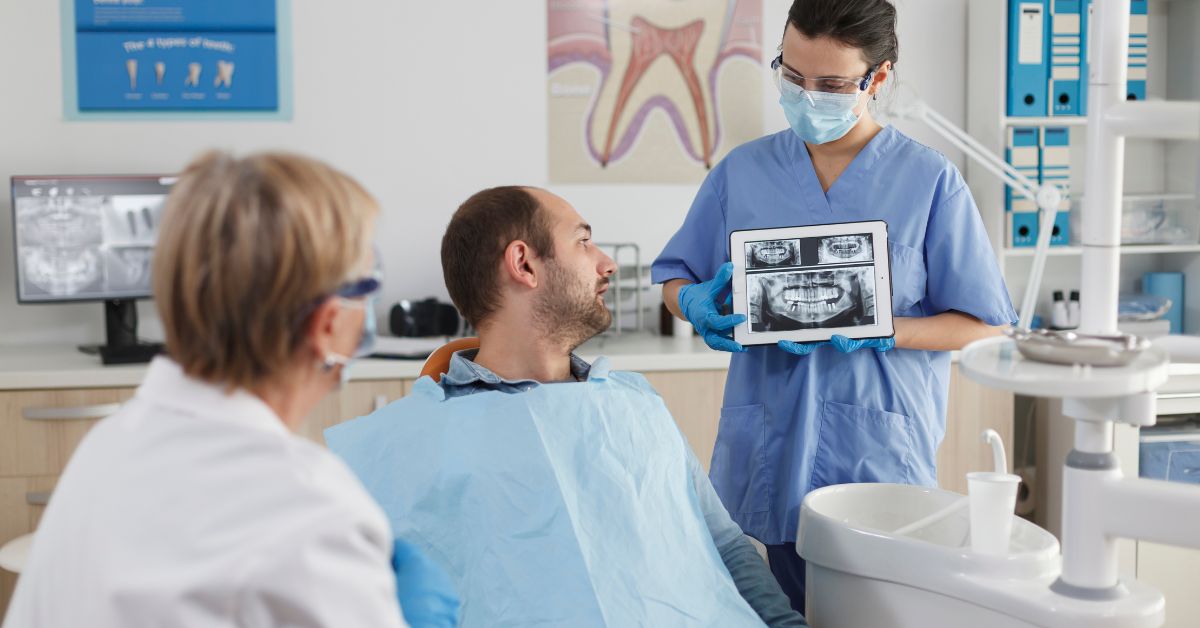
When dealing with serious dental issues, it’s essential to know which dental professional to consult. Two common specialists people confuse are endodontists and oral surgeons. Although both are crucial in dental health, they serve different purposes. This guide will break down everything you need to know about the differences between an endodontist and an oral surgeon, helping you decide who to visit based on your specific condition.
What Is an Endodontist?
An endodontist is a dental specialist focused primarily on the diagnosis and treatment of issues within the tooth pulp and nerves. These professionals are often called “root canal specialists” because that’s their main procedure. Endodontists receive additional training after dental school—usually two or more years—to specialize in treating tooth pain and performing root canal therapy.
They use advanced techniques and equipment such as dental microscopes and 3D imaging to treat intricate tooth structures. Their main goal is to save your natural teeth whenever possible. Most general dentists refer complex root canal cases to endodontists.
Endodontists are less involved in surgical procedures outside of the tooth’s interior. If your tooth is cracked internally or the pulp is infected, they are the experts to handle it.
What Is an Oral Surgeon?
Oral surgeons, also known as oral and maxillofacial surgeons, are dental professionals trained in complex surgeries involving the mouth, face, and jaw. Their expertise goes beyond the teeth—they perform surgeries on bones, tissues, and facial structures. These specialists undergo 4-6 years of hospital-based surgical training after dental school.
They commonly handle:
-
Wisdom tooth removal
-
Jaw realignment
-
Facial trauma repair
-
Cyst or tumor removal
-
Dental implants
-
Biopsies
If your dental problem involves surgery outside the scope of a general dentist or endodontist, an oral surgeon is the professional you need.
Key Differences Between Endodontists and Oral Surgeons
-
Scope of Practice:
-
Endodontist: Root canals, internal tooth issues
-
Oral Surgeon: Extractions, jaw surgery, implants
-
-
Type of Care:
-
Endodontist: Conservative, tooth-preserving
-
Oral Surgeon: Surgical, invasive procedures
-
-
Tools and Techniques:
-
Endodontist: Microscopes, irrigation, endodontic files
-
Oral Surgeon: Scalpels, sutures, surgical drills
-
-
Settings:
-
Endodontists: Work in private dental practices
-
Oral Surgeons: Often work in hospitals and surgical centers
-
Common Procedures Performed by Each Specialist
Endodontist Procedures:
-
Retreatment of failed root canals
-
Apicoectomy (root end surgery)
-
Cracked tooth diagnosis
-
Treatment of dental abscesses
Oral Surgeon Procedures:
-
Wisdom tooth extraction
-
Jawbone surgery
-
Dental implant placement
-
Reconstructive surgery
-
TMJ surgery
When Should You See an Endodontist or Oral Surgeon?
Knowing the right time to consult an endodontist or an oral surgeon can prevent unnecessary pain and ensure you receive the most appropriate treatment. If you’re experiencing deep tooth pain, prolonged sensitivity to hot or cold, or discomfort when biting or chewing, it may be time to visit an endodontist. These symptoms often indicate problems with the tooth’s pulp or nerve tissue, and endodontists are specialists in diagnosing and treating such internal issues through procedures like root canal therapy.
On the other hand, if your dental problem involves complex oral surgery, you should consider seeing an oral surgeon. This includes situations like impacted wisdom teeth, jaw misalignment, facial trauma, or the need for dental implants. Oral surgeons are also trained to manage surgical interventions for tumors, cysts, or severe infections that require more than routine dental care.
Timing is crucial. Visiting the wrong specialist can delay effective treatment and increase discomfort. Always start with your general dentist, who can evaluate your symptoms and recommend the right course of action—whether it’s saving your natural tooth with an endodontist or undergoing a surgical procedure with an oral surgeon.
Training and Education Requirements
Both specialists complete dental school, but their post-graduate paths diverge:
-
Endodontist: 2-3 years in endodontic residency
-
Oral Surgeon: 4-6 years in hospital surgical residency
This extra training equips them to handle their specific cases with precision.
How Can a Father Lose Visitation Rights? (Contextual SEO Integration)
Though not directly dental, it’s important for healthcare professionals (like oral surgeons dealing with child patients) to be aware of family legal dynamics. A father can lose visitation rights due to reasons like abuse, neglect, endangerment, or court violation. This is especially relevant when child patients must be accompanied only by approved guardians during procedures.
Cost Comparison and Insurance Considerations
Endodontist Costs:
-
Typically ranges from $700 to $1,500 per root canal
-
Insurance may cover part or all of the procedure
-
Lower overall cost if the tooth is saved
Oral Surgeon Costs:
-
Extractions: $200 to $600
-
Implants: $2,000 to $5,000
-
May require anesthesia, adding to the cost
-
Insurance coverage varies widely
Choosing the Right Specialist for Your Needs
Ask Yourself These Questions:
-
Is your pain internal or external to the tooth?
-
Has your dentist recommended surgery?
-
Do you want to save the tooth or remove it?
-
Does your insurance cover the specialist?
Make sure to ask your general dentist for a referral and consider getting a second opinion before any major procedure.
FAQs
1. Can an endodontist extract teeth?
Yes, but only in special cases. They focus on saving teeth, not removing them.
2. Are root canals painful with an endodontist?
Modern root canal treatments are relatively pain-free, thanks to advanced anesthesia and techniques.
3. Do oral surgeons perform cosmetic procedures?
Yes, they can perform cosmetic surgeries related to the face and jaw, such as corrective jaw surgery.
4. Will my insurance cover oral surgery?
It depends on your policy. Medical insurance may cover surgeries involving trauma, while dental insurance may cover extractions or implants.
5. How do I know if I need an endodontist or oral surgeon?
Start with your general dentist. They will assess your condition and refer you to the appropriate specialist.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between an endodontist and an oral surgeon is essential for choosing the right dental care. If you’re experiencing tooth pain, internal issues, or need a root canal, an endodontist is your go-to specialist. But if the problem involves surgery or facial trauma, you’ll need the expertise of an oral surgeon. Always consult with your general dentist to help direct you to the right professional, ensuring your oral health is handled with the care it deserves.